How to Calculate Opportunity Cost with Formula
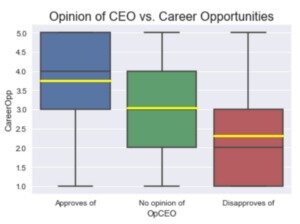
The trade-off, however, is that you can’t withdraw these funds for the entire five-year period. Opportunity cost describes the difference between the value of one alternative and the value of the next best alternative. Below, we’ve used the formula to work through situations business founders are likely to encounter.
Opportunity Cost: What Is It and How to Calculate It – The Balance
Opportunity Cost: What Is It and How to Calculate It.
Posted: Fri, 30 Dec 2022 08:00:00 GMT [source]
This can be done during the decision-making process by estimating future returns. Alternatively, the opportunity cost can be calculated with hindsight by comparing returns since the decision was made. As you have seen, every action you’ll take has an opportunity cost. You should always compare every economic opportunity and choose the option with minimal costs.
Est. closing costs
We recommend beginning with your Zestimate, Zillow’s best estimate of your home’s market value. The Zestimate is based on a blend of valuation methods, with a median error rate of 3.5%. You see that a supplier charges $10 for a certain part—and that’s your cost.
We’ll walk through some opportunity cost examples and give you tips to apply them to your business. You’ll also learn how opportunity costs, sunk costs, and risks are different. Working with limited resources is one of the challenges that entrepreneurs must learn to love.
It’s important to understand opportunity cost because it allows you to see opportunities you missed out on and how they compare the opportunities that you took, whether it be for better or for worse. Say you are presented with two investment opportunities, but you can only afford to invest in one. You need to analyze the situation and invest in the opportunity that makes the most financial sense both in the short term and the long term. Imagine you enjoyed the taco tremendously—and you make a habit of purchasing the same taco every single day.
#2. Accounting Profit / Loss
Opportunity cost figures can give you insight into the direction you want to go in and guide your financial decision-making. On the other hand, opportunity cost relates to the idea that the returns of a chosen investment will potentially be lower than the returns of the next best option. Investing in securities products involves risk and you could lose money. Brex Treasury is not a bank nor an investment adviser and your Brex business account is not an FDIC-insured bank account.
- Still, one could consider opportunity costs when deciding between two risk profiles.
- However, it shows you how money can be easily spent on something that can take away from other opportunities, whether they have to do with investing or not.
- Many homeowners avoid capital gains taxes when selling their primary home by qualifying for the capital gains tax exemption.
- As mentioned, opportunity cost is a comparison used to help investors, or anyone really, make intelligent financial decisions.
People like to think cash is king, he says, but holding exclusively dollar bills long term all but ensures you’ll experience large opportunity losses. The basic formula for opportunity cost is the same in academic economics as it is in everyday use—it’s just expressed differently. Opportunity costs may have explicit financial costs, like when you choose to use your dollars for one thing instead of another, or implicit costs.
Time Poverty: What To Do If You Feel Time Poor
He decides to close his office one afternoon to paint the office himself, thinking that he’s saving money on the costs of hiring professional painters. However, the painting took him four hours, effectively costing him $1,600 in lost wages. Let’s say professional painters would have charged Larry $1,000 for the work. An investor calculates the opportunity cost by comparing the returns of two options.

At the end of the month, your friend invites you to go out for drinks—but you can’t afford to go out because you have continuously spent money on tacos throughout the month. Not being able to purchase a smoothie was your short-term opportunity cost. Now, not being able to go out for drinks is your long-term opportunity cost. And that’s not even considering inflation, or the steady loss in purchasing power cash falls victim to over time. If you choose to stay in cash long term, not only are you missing out on the opportunity to grow that money in the stock market, but your dollars are also losing value by around 2% each year.
Formula and Calculation of Opportunity Cost
Now we have an equation that helps us calculate the number of burgers Charlie can buy depending on how many bus tickets he wants to purchase in a given week. For instance, assume that the firm described above has invested $30 billion to start its operations. However, a fall in demand for oil products has led to a foreseeable revenue of $50 billion.
Is There An Opportunity With Johnson & Johnson’s (NYSE:JNJ) 24% Undervaluation? – Yahoo Finance
Is There An Opportunity With Johnson & Johnson’s (NYSE:JNJ) 24% Undervaluation?.
Posted: Sun, 30 Jul 2023 12:00:34 GMT [source]
Capital structure may involve a mix of long-term debt, short-term debt, and equity. Equity is the infusion of capital into a business through the sale of shares of common stock or preferred stock to investors. This information is not intended as a recommendation to invest in any particular asset class or strategy or as a promise of future performance. There is no guarantee that any investment strategy will work under all market conditions or is suitable for all investors. Each investor should evaluate their ability to invest long term, especially during periods of downturn in the market. Investors should not substitute these materials for professional services, and should seek advice from an independent advisor before acting on any information presented.
Opportunity Cost Treatment: Accounting Profit vs. Economic Profit
Without this type of calculation, you may make a decision that appears to be the best choice on the surface—but actually isn’t efficient in the long run. There’s no doubt that investing can be a nerve-wracking and tricky business. However, with the right precautions, it can also be extremely profitable. To minimize risks and maximize profits, investors often use various tricks of the trade to calculate and compare potential decisions. In other words, if the investor chooses Company A, they give up the chance to earn a better return under those stock market conditions. Although some investors aim for the safest return, others shoot for the highest payout.
You can use risk when trying to figure out your opportunity cost. It allows you to see the performance of certain investments and determine which choice might be less risky when it comes to returns. However, sometimes the less risky option comes with fewer returns. Many people wonder about the difference cash fund management finance & accounting between opportunity cost and sunk cost. Opportunity cost is the potential returns not earned in the future because you decided to invest in another place. You can look at two investment opportunities subjectively and then decide which one is the best for you in the current situation.
- Thanks to this tool, you will be able to calculate how much money you will earn by investing the money instead of spending it on goods or services, and from this find out what the opportunity cost is.
- When you think of opportunity cost in this manner, everything becomes easy.
- Let’s look at an example on how a business can use opportunity cost analysis to determine whether or not obtaining an infusion of capital through debt is a smart move.
- Investment advisory services are only provided to investors who become Stash Clients pursuant to a written Advisory Agreement.
- B on the other hand requires you to tie your money for seven years but presents a higher interest.
- By building a DCF model in Excel, the analyst is able to compare different projects and assess which is most attractive.
This information should not be relied upon by the reader as research or investment advice regarding any issuer or security in particular. There is no guarantee that any strategies discussed will be effective. In this case, you can consider an investment’s opportunity cost by weighing the potential pros and cons of investing in a bond, versus the pros and cons of investing in a stock.
When and Where Opportunity Cost Calculations Are Useful
Over the next 50 years, this investor dutifully invested $5,000 per year in bonds, achieving an average annual return of 2.50% and retiring with a portfolio worth nearly $500,000. Although this result might seem impressive, it is less so when one considers the investor’s opportunity cost. Let’s say that in Country A, we can either produce 50 tons of corn, or as an alternative, we can produce 25 tons of beef. Now we have all the information we need to calculate opportunity cost, but we need to know which opportunity cost we’re trying to measure based on which possibility we want to choose.
Once we understand the basics, we can move onto applying the concept to make better business decisions. Johnson points to historical data on stocks versus bonds to illustrate the missed financial opportunities. From 1926 to 2020, large capitalization stocks, like those in the S&P 500, have seen average annual returns of 10.2%. Long-term government bonds averaged 5.5% annually whereas Treasury Bills returned 3.3% each year on average. Whether it means investing in one stock over another or simply opting to study for a big math exam instead of meeting a friend for pizza, opportunity cost pervades every facet of life.
Calculating opportunity cost can be difficult because not all future variables can be known in the present moment. “This reduces the investor’s decisions from looking at every opportunity to a manageable question of ‘How much of each asset class should I hold? Ultimately, no matter what your current circumstances may be, it’s never too late to start using opportunity cost as a tool for setting and achieving future financial goals. You have to consider time lost, wages lost, college cost, and the potential earnings increase you might see after achieving your degree.
Let’s look at how to calculate opportunity cost using land as an example. In country A, we can use the same amount of scarce resources to produce two things, but we can only choose one thing at a time to produce. You chose to read this article instead of reading another article, checking your Facebook page, or watching television. Your life is the result of your past decisions, and that, essentially, is the definition of opportunity cost. Here is the way to calculate opportunity cost, along with some ways it can be used to inform your investment decisions and more. Assume that you have to choose between two investments, Option A and B.
A large part of her decision-making analysis will concern calculating and assessing opportunity cost. You receive a call from a notary one morning telling you that you inherited $100,000 from a distant, wealthy relative. You are so happy with this surprise – Finally, a path to wealth! You wish to invest this money for a year before using the proceeds to put a down payment on a house.





